Prior to initiation of the physical random access procedure, Layer 1:
- receives from higher layers a set of SS/PBCH block indexes and provides to higher layers a corresponding set of RSRP measurements
- receives the following information from the higher layers
- Configuration of physical random access channel (PRACH) transmission parameters (PRACH preamble format, time resources, and frequency resources for PRACH transmission).
- Parameters for determining the root sequences and their cyclic shifts in the PRACH preamble sequence set (index to logical root sequence table, cyclic shift ( CS N ), and set type (unrestricted, restricted set A, or restricted set B)).
From the physical layer perspective, the L1 random access procedure includes:
- transmission of random access preamble (MSG1) in a PRACH
- random access response (RAR) message with a PDCCH/PDSCH (MSG2)
- when applicable, transmission of a PUSCH scheduled by a RAR UL grant
- when applicable, PDSCH for contention resolution
If a random access procedure is initiated by a PDCCH order to the UE, a PRACH transmission is with a same SCS as a PRACH transmission initiated by higher layers.
If a UE is configured with two UL carriers for a serving cell and the UE detects a PDCCH order, the UE uses the UL/SUL indicator field value from the detected PDCCH order to determine the UL carrier for the corresponding PRACH transmission.
Contention-based vs Contention-free Random Access
There are two categories of Random Access procedure:
- Contention Based Random Access (CBRA): allows the UE to select a random access preamble from a pool shared with other UEs. There are risks that multiple UEs may select the same preamble. What happens when multiple UEs select the same preamble:
- these UEs will decode the same content from RAR (MSG2)
- these UEs will transmit MSG3 using the same set of RBs and symbols
- BS will decode one of those MSG3, and will complete contention resolution:
- if MSG3 included a CCCH message: contention resolution achieved based on MAC CE within MSG4
- if MSG3 indluded a DCCH message or DTCH data: conteition resolution achieved addressing the UE on the PDCCH by its C-RNTI
- One UE will complete the Random Access procedure, remaining UEs will continue the procedure by selecting another preamble
- Contention Free Random Access (CFRA): base station allocates a dedicated random access preamble beforehand, thus, ensures different UEs use different preambles. The preamble is provided using either RRC signaling by ra-PreambleIndex, or Layer 1 signaling (within DCI on the PDCCH)
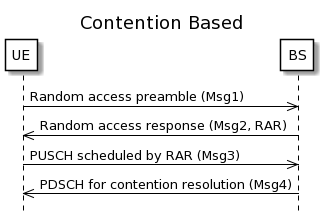

Table below sumarizes the possible cases of random access, and the choices of contention resolution types. Note that, Contention-based Random Access can be used in all the cases.
| Possible cases | Contention-based | Contention-free | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial access from RRC Idle state | ✓ | - | UE: send RRCSetupRequest in MSG3 |
| Transition from RRC Inactive to RRC Connected | ✓ | - | UE: send RRCResumeRequest in MSG3 |
| RRC Connection re-establishment | ✓ | - | UE: send RRCReestablishmentRequest in MSG3 |
| Handover | ✓ | ✓ | BS: provide preamble using RACH-ConfigDedicated within RRCReconfiguration UE: send RRCReconfigurationComplete in MSG3 |
| Downlink data arrival while UE is out of sync | ✓ | ✓ | BS: signal a PDCCH-Order using DCI format 1_0, with (contention-free) or without (contention-based) preamble index UE: for contention resolution, include a C-RNTI MAC CE in MSG3 |
| Uplink data arrival while UE is out of sync | ✓ | - | UE: for contention resolution, include a C-RNTI MAC CE in MSG3 |
| Uplink data arrival for UE without PUSCH resource allocation | ✓ | - | UE: for contention resolution, include a C-RNTI MAC CE in MSG3. MSG3 may include a BSR MAC CE to request additional uplink resource |
| On-demand system information | ✓ (MSG3 based) | ✓ (MSG1 based) |
|
| Beam failure recover | ✓ | ✓ | Contention-based: UE selects a PRACH preamble corresponding to the SSB beam for recovery Contention-free: BS provide UE with one PRACH preamble index for each beam available for recovery |
| Scheduling request failure | ✓ | - | UE use Random Access if BS does not provide an uplink grant after sr-TransMax (4 to 64) Scheduling Requests |
| Synchronous reconfiguration | ✓ | ✓ | BS: trigger synchronous reconfiguration by including reconfigurationWithSync within RRCReconfiguration UE: perform contention-based (ra-PreambleIndex excluded from reconfigurationWithSync) or contention-free (ra-PreambleIndex included in reconfigurationWithSync) Random Access |
| Establishing time alignment during Scell addition | ✓ | ✓ | used to initialize Timing Advance of a newly added SCell belong to a new Timing Advance Group (TAG). Contention-based on contention-free depends on if ra-PreambleIndex is excluded from reconfigurationWithSync |